
Atomic radius of o series#
Inner Transition Elements: The density of these elements increases much more in the f series because of.Therefore, the transition elements lie at the minima of the atomic volume curve in the respective periods, At the d 10 configuration, the size increases abruptly due to the completion of subshell and the density decreases. Transition Elements: When electrons are added in the d orbitals, the density of the element increases due to the decrease in their atomic radii.Their density decreases and consequently, their atomic volumes increase. However, with further increase in the valence shell electrons, the metallic character decreases and the elements become nonmetallic.
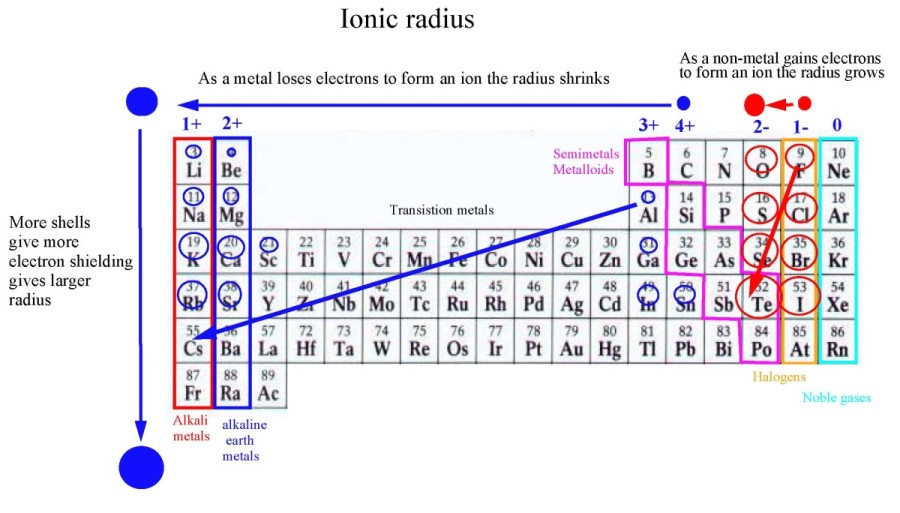
As a result, the density of the elements increases and their atomic volume decreases.
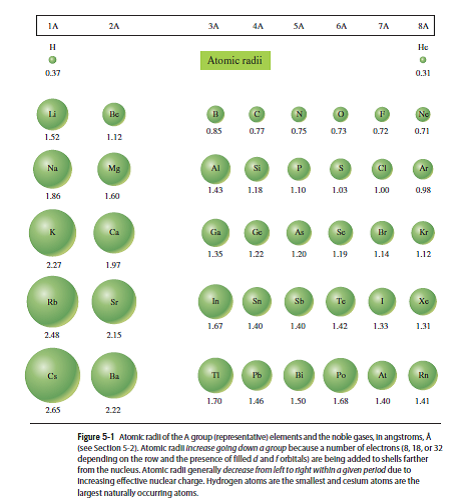 Variation along a Period for Representative Elements: As electrons are added in the valence shell, there is a decrease in atomic sizes and increase in the metallic character of elements with increasing nuclear charge after group 1. Therefore, they have a large atomic volume and are at local maxima in the curve. Also, they form a more open body-centered (bcc) lattice. Alkali metals: Due to the formation of a new quantum shell of electrons, the alkali metals have a much larger radius than the preceding halogens. įigure (4.3).1 Variation of Atomic Volume against atomic number Z When AV is plotted against atomic number Z, following trends are observed. In spite of the limitations, atomic volumes of elements show some characteristic periodic trends. (4.3).1.2 Variation of Atomic Volume with Atomic Number Density of a substance depends on the temperature and decreases with increase in temperature. Different allotropes have different densities due to the different arrangement of atoms. Many elements like carbon, sulphur, phosphorus, tin or arsenic exist in allotropic forms. The fcc or ccp structures are close-packed structures and have less vacant space, while others like bcc are more open structures with more vacant space in its lattice. Atomic volume strongly depends on the structure adopted by the element in solid state. The volume of one mole of X n molecules cannot be considered to be equal to n times the volume of a mole of X atoms either at molecular level or in solid state. Elements have different atomicity, e.g., He, Ne, Ar, H 2, O 2 ,N 2, P 4, As 4, S 8, etc. Where V sp is the specific volume of element, defined as the volume occupied by 1 kg of element in liters.Ītomic volume of Avogadro number of atoms ( not molecules) of an element depends upon a number of factors, which reduce the usefulness of the concept. If ρ is the density of an element having atomic mass A, then
Variation along a Period for Representative Elements: As electrons are added in the valence shell, there is a decrease in atomic sizes and increase in the metallic character of elements with increasing nuclear charge after group 1. Therefore, they have a large atomic volume and are at local maxima in the curve. Also, they form a more open body-centered (bcc) lattice. Alkali metals: Due to the formation of a new quantum shell of electrons, the alkali metals have a much larger radius than the preceding halogens. įigure (4.3).1 Variation of Atomic Volume against atomic number Z When AV is plotted against atomic number Z, following trends are observed. In spite of the limitations, atomic volumes of elements show some characteristic periodic trends. (4.3).1.2 Variation of Atomic Volume with Atomic Number Density of a substance depends on the temperature and decreases with increase in temperature. Different allotropes have different densities due to the different arrangement of atoms. Many elements like carbon, sulphur, phosphorus, tin or arsenic exist in allotropic forms. The fcc or ccp structures are close-packed structures and have less vacant space, while others like bcc are more open structures with more vacant space in its lattice. Atomic volume strongly depends on the structure adopted by the element in solid state. The volume of one mole of X n molecules cannot be considered to be equal to n times the volume of a mole of X atoms either at molecular level or in solid state. Elements have different atomicity, e.g., He, Ne, Ar, H 2, O 2 ,N 2, P 4, As 4, S 8, etc. Where V sp is the specific volume of element, defined as the volume occupied by 1 kg of element in liters.Ītomic volume of Avogadro number of atoms ( not molecules) of an element depends upon a number of factors, which reduce the usefulness of the concept. If ρ is the density of an element having atomic mass A, then 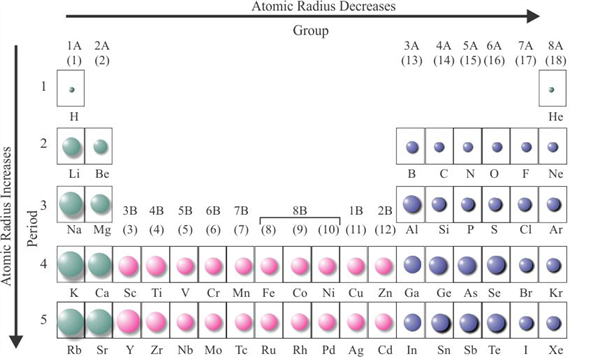
( G S Manku, email: (4.3).1 ATOMIC VOLUME (4.3).1.1 DefinitionĪtomic volume (AV), also called the gram atomic volume, for an element, is defined as the volume occupied by 1 mole or Avogadro number of atoms of the element.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
